Your cart is currently empty!
Written by Riyan Sharma {08|08|2025}
Space Tourism
Space Tourism
Once a dream reserved for astronauts and sci-fi movie heroes, space tourism is now on the verge of becoming a reality — a leap as significant as the first airplane flight in the early 1900s. With private companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic leading the way, everyday people (albeit those with substantial wealth) can now secure a seat to the stars, complete with training programs, safety briefings, and even custom space suits. The 2020s might go down in history as the decade when humans truly became a spacefaring species, taking our first commercial steps beyond Earth’s atmosphere and opening the door to a future where vacations might include zero-gravity dining and sunrise over the Moon.
“In the future, going to space could be as common as flying to another country.” – Elon Musk

From Sci-Fi to Reality
Then: Space travel was mostly confined to the realms of books, films, and imaginative dreams – think Star Trek, Interstellar, and countless sci-fi novels where humans casually roamed the galaxy.
Now: Successful suborbital and orbital flights with civilians onboard are not only proving it’s possible but also paving the way for a new era of commercial space exploration. These missions demonstrate the growing capabilities of private companies and the tangible shift from science fiction to reality.
Milestones:
2001: First space tourist (Dennis Tito) visited the ISS, marking humanity’s initial step toward leisure travel beyond Earth.
2021: Blue Origin & Virgin Galactic carried paying passengers into space, offering minutes of weightlessness and breathtaking views.
2023: SpaceX completed the all-civilian Inspiration4 orbital mission, spending days circling the Earth without professional astronauts onboard.
Different Space Tourism
| Type | Duration | Height | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suborbital | 10–15 minutes | 100 km above Earth | Weightlessness & view of Earth’s curve |
| Orbital | Several days | 400 km+ (ISS orbit) | Living in microgravity, space views |
| Lunar/Deep Space | Days–Weeks | 384,000 km+ | Flybys of Moon, deep space views |
Major Players in Space Tourism
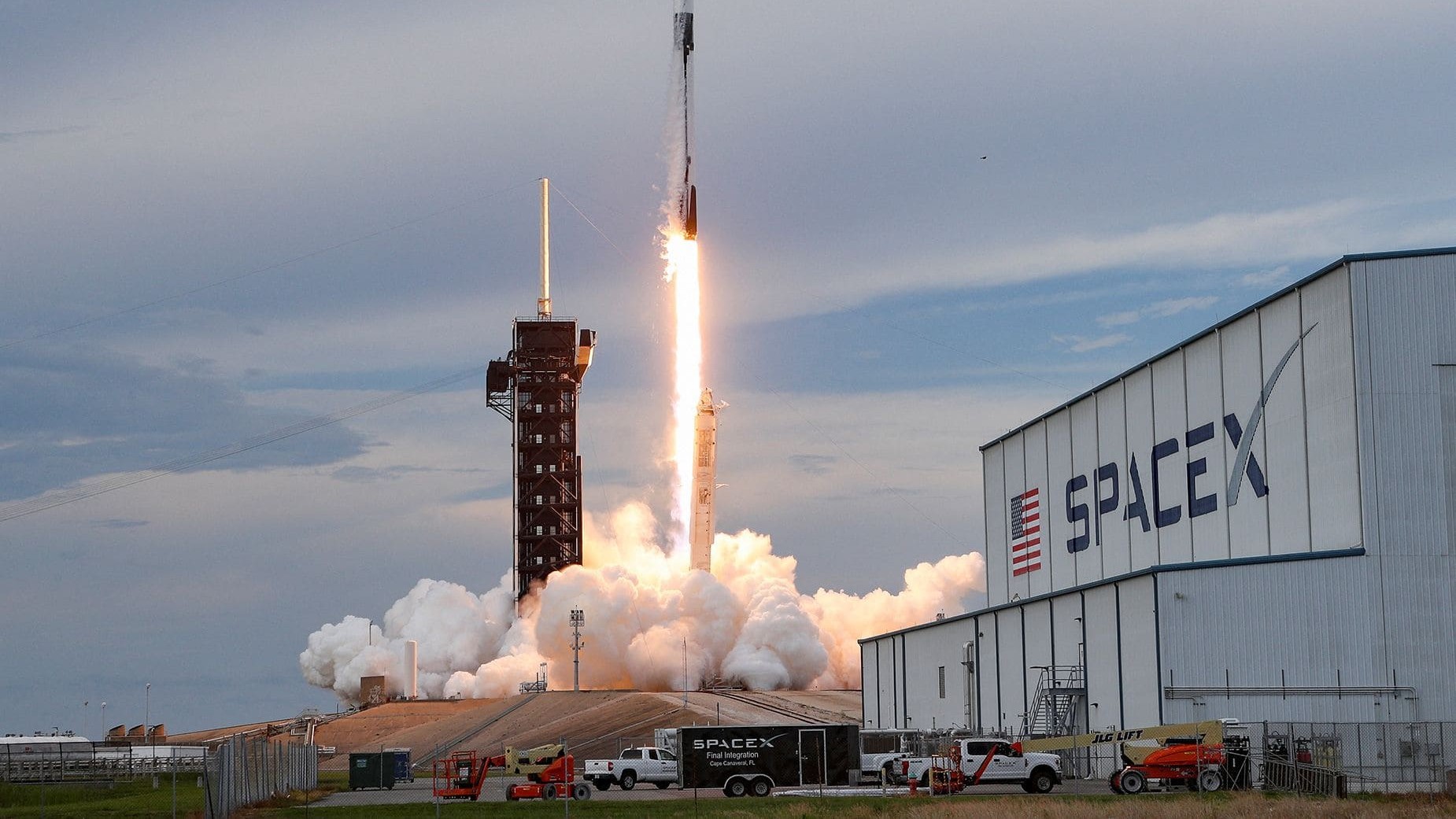
SpaceX
Plans ambitious lunar tourism missions via Starship, aiming to take private passengers on multi-day journeys around the Moon complete with unparalleled views and unique training programs.
Already sent civilians into orbit, demonstrating its capability for long-duration crewed flights and setting the stage for even more advanced tourism ventures.

Blue Origin
New Shepard suborbital flights offer short yet thrilling trips to the edge of space, giving passengers several minutes of weightlessness and stunning panoramic views of Earth from above.
The program is focused on accessibility and frequent launches, aiming to make such experiences available to more customers over time by reducing costs, increasing launch cadence, and improving training for first-time space travelers.
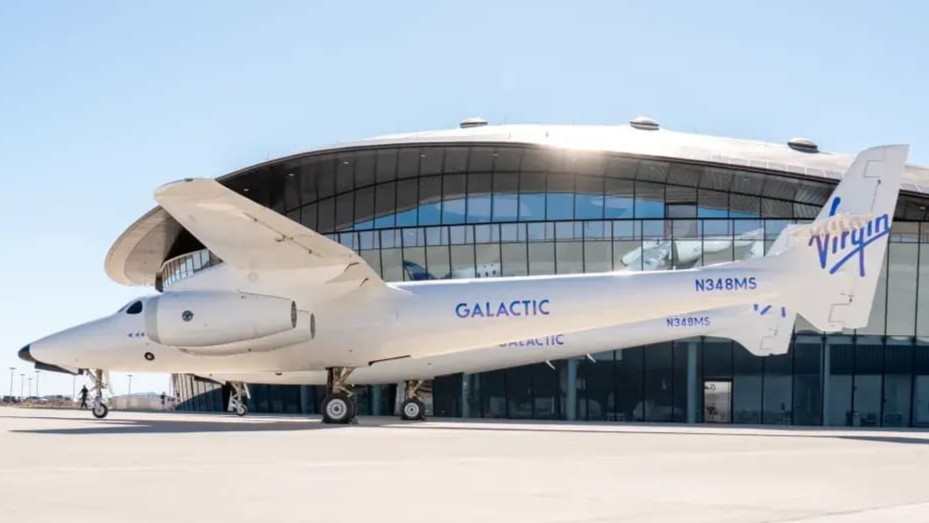
Virgin Galactic
VSS Unity offers suborbital tourism with a luxury experience that blends the thrill of reaching the edge of space with high-end comfort, personalized service, and breathtaking panoramic views, ensuring that passengers enjoy both an unforgettable adventure and a premium, pampered journey from takeoff to landing.

Cost & Who Can Go
Currently, space tourism is ultra-premium:
- Suborbital flights: $250,000 – $450,000 per seat.
- Orbital missions: $50M – $70M per passenger.
- Lunar missions: Expected over $100M.
“Right now, it’s for the ultra-wealthy — but prices could drop in 20–30 years, making it accessible to more people.”
Impact on Science & Tech
Boosts Innovation – Accelerates the development of reusable rockets and advanced propulsion systems, pushing the limits of what’s technologically possible in space exploration.
Inspires Future Scientists – Motivates students and young innovators by giving them tangible examples of real-life space travel, sparking interest in STEM fields and encouraging new research initiatives.
New Industries – Lays the groundwork for entire sectors such as space hotels, asteroid mining, satellite servicing, and even orbital manufacturing facilities that could revolutionize economies both on Earth and in space.
Impact on Science & Tech

Boosts Innovation – Accelerates the development of reusable rockets and advanced propulsion systems, pushing the limits of what’s technologically possible in space exploration.
Inspires Future Scientists – Motivates students and young innovators by giving them tangible examples of real-life space travel, sparking interest in STEM fields and encouraging new research initiatives.
New Industries – Lays the groundwork for entire sectors such as space hotels, asteroid mining, satellite servicing, and even orbital manufacturing facilities that could revolutionize economies both on Earth and in space.
Concerns & Criticism

Environmental Impact – Rocket launches emit significant CO₂ and other greenhouse gases, contributing to atmospheric pollution and potential long-term climate effects, especially with the increasing frequency of flights.
Safety Risks – Space travel remains dangerous, with the inherent risks of rocket malfunctions, exposure to radiation, and the harsh environment of space making every mission a high-stakes endeavor.
Economic Inequality – Often seen as a playground for billionaires, it underscores the gap between the wealthy elite who can afford such trips and the majority of people on Earth, raising questions about resource allocation and fairness.

The Future of Space Travel
In just 20–30 years, the landscape of travel could be unrecognizable compared to today. We might witness:
1. Space Hotels orbiting in low Earth orbit, complete with panoramic observation decks, zero-gravity sports arenas, and fine-dining restaurants serving gourmet meals while Earth spins below.
2. Lunar Resorts designed for luxury vacations, offering guided tours of the Moon’s surface, rover excursions to craters, and exclusive opportunities to witness Earthrise from the lunar horizon.
3. Commercial Mars Trips for daring explorers, with months-long journeys to the Red Planet, immersive training beforehand, and the chance to be among the first humans to step onto Martian soil.
Beyond these visions, there could be orbital theme parks, asteroid-mining tours for adventurous entrepreneurs, and even space-based retirement communities for those seeking a cosmic view in their golden years. Some market analysts predict that by 2050, space tourism could evolve into a $1 trillion industry, with thousands of jobs created in spacecraft maintenance, hospitality, entertainment, and interplanetary logistics. This growth could mirror the aviation boom of the 20th century — but on a much grander, galactic scale.
Space tourism is no longer just a futuristic fantasy, it’s the dawn of a new era in human exploration and travel. As private companies continue to innovate and push boundaries, the possibility of ordinary people experiencing the wonders of space is becoming more tangible every year. While there are still challenges such as high costs, safety concerns, and environmental impacts, the potential benefits, from inspiring global unity to advancing scientific research, are immense. This next great leap in travel will not only reshape how we vacation but also how we view ourselves as inhabitants of a small, fragile planet in a vast and awe-inspiring universe. The countdown has begun, and the journey to the stars is no longer a question of “if,” but “when.”
Written by Riyan Sharma {08|08|2025}
Space Tourism
Space Tourism
Once a dream reserved for astronauts and sci-fi movie heroes, space tourism is now on the verge of becoming a reality — a leap as significant as the first airplane flight in the early 1900s. With private companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic leading the way, everyday people (albeit those with substantial wealth) can now secure a seat to the stars, complete with training programs, safety briefings, and even custom space suits. The 2020s might go down in history as the decade when humans truly became a spacefaring species, taking our first commercial steps beyond Earth’s atmosphere and opening the door to a future where vacations might include zero-gravity dining and sunrise over the Moon.
“In the future, going to space could be as common as flying to another country.” – Elon Musk

From Sci-Fi to Reality
Then: Space travel was mostly confined to the realms of books, films, and imaginative dreams – think Star Trek, Interstellar, and countless sci-fi novels where humans casually roamed the galaxy.
Now: Successful suborbital and orbital flights with civilians onboard are not only proving it’s possible but also paving the way for a new era of commercial space exploration. These missions demonstrate the growing capabilities of private companies and the tangible shift from science fiction to reality.
Milestones:
2001: First space tourist (Dennis Tito) visited the ISS, marking humanity’s initial step toward leisure travel beyond Earth.
2021: Blue Origin & Virgin Galactic carried paying passengers into space, offering minutes of weightlessness and breathtaking views.
2023: SpaceX completed the all-civilian Inspiration4 orbital mission, spending days circling the Earth without professional astronauts onboard.
Different Space Tourism
| Type | Duration | Height | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suborbital | 10–15 minutes | 100 km above Earth | Weightlessness & view of Earth’s curve |
| Orbital | Several days | 400 km+ (ISS orbit) | Living in microgravity, space views |
| Lunar/Deep Space | Days–Weeks | 384,000 km+ | Flybys of Moon, deep space views |
Major Players in Space Tourism
SpaceX
Plans ambitious lunar tourism missions via Starship, aiming to take private passengers on multi-day journeys around the Moon complete with unparalleled views and unique training programs.
Already sent civilians into orbit, demonstrating its capability for long-duration crewed flights and setting the stage for even more advanced tourism ventures.

Blue Origin
New Shepard suborbital flights offer short yet thrilling trips to the edge of space, giving passengers several minutes of weightlessness and stunning panoramic views of Earth from above.
The program is focused on accessibility and frequent launches, aiming to make such experiences available to more customers over time by reducing costs, increasing launch cadence, and improving training for first-time space travelers.

Virgin Galactic
VSS Unity offers suborbital tourism with a luxury experience that blends the thrill of reaching the edge of space with high-end comfort, personalized service, and breathtaking panoramic views, ensuring that passengers enjoy both an unforgettable adventure and a premium, pampered journey from takeoff to landing.

Cost & Who Can Go
Currently, space tourism is ultra-premium:
- Suborbital flights: $250,000 – $450,000 per seat.
- Orbital missions: $50M – $70M per passenger.
- Lunar missions: Expected over $100M.
“Right now, it’s for the ultra-wealthy — but prices could drop in 20–30 years, making it accessible to more people.”
Impact on Science & Tech
Boosts Innovation – Accelerates the development of reusable rockets and advanced propulsion systems, pushing the limits of what’s technologically possible in space exploration.
Inspires Future Scientists – Motivates students and young innovators by giving them tangible examples of real-life space travel, sparking interest in STEM fields and encouraging new research initiatives.
New Industries – Lays the groundwork for entire sectors such as space hotels, asteroid mining, satellite servicing, and even orbital manufacturing facilities that could revolutionize economies both on Earth and in space.
Impact on Science & Tech

Boosts Innovation – Accelerates the development of reusable rockets and advanced propulsion systems, pushing the limits of what’s technologically possible in space exploration.
Inspires Future Scientists – Motivates students and young innovators by giving them tangible examples of real-life space travel, sparking interest in STEM fields and encouraging new research initiatives.
New Industries – Lays the groundwork for entire sectors such as space hotels, asteroid mining, satellite servicing, and even orbital manufacturing facilities that could revolutionize economies both on Earth and in space.
Concerns & Criticism

Environmental Impact – Rocket launches emit significant CO₂ and other greenhouse gases, contributing to atmospheric pollution and potential long-term climate effects, especially with the increasing frequency of flights.
Safety Risks – Space travel remains dangerous, with the inherent risks of rocket malfunctions, exposure to radiation, and the harsh environment of space making every mission a high-stakes endeavor.
Economic Inequality – Often seen as a playground for billionaires, it underscores the gap between the wealthy elite who can afford such trips and the majority of people on Earth, raising questions about resource allocation and fairness.

The Future of Space Travel
In just 20–30 years, the landscape of travel could be unrecognizable compared to today. We might witness:
1. Space Hotels orbiting in low Earth orbit, complete with panoramic observation decks, zero-gravity sports arenas, and fine-dining restaurants serving gourmet meals while Earth spins below.
2. Lunar Resorts designed for luxury vacations, offering guided tours of the Moon’s surface, rover excursions to craters, and exclusive opportunities to witness Earthrise from the lunar horizon.
3. Commercial Mars Trips for daring explorers, with months-long journeys to the Red Planet, immersive training beforehand, and the chance to be among the first humans to step onto Martian soil.
Beyond these visions, there could be orbital theme parks, asteroid-mining tours for adventurous entrepreneurs, and even space-based retirement communities for those seeking a cosmic view in their golden years. Some market analysts predict that by 2050, space tourism could evolve into a $1 trillion industry, with thousands of jobs created in spacecraft maintenance, hospitality, entertainment, and interplanetary logistics. This growth could mirror the aviation boom of the 20th century — but on a much grander, galactic scale.
Space tourism is no longer just a futuristic fantasy, it’s the dawn of a new era in human exploration and travel. As private companies continue to innovate and push boundaries, the possibility of ordinary people experiencing the wonders of space is becoming more tangible every year. While there are still challenges such as high costs, safety concerns, and environmental impacts, the potential benefits, from inspiring global unity to advancing scientific research, are immense. This next great leap in travel will not only reshape how we vacation but also how we view ourselves as inhabitants of a small, fragile planet in a vast and awe-inspiring universe. The countdown has begun, and the journey to the stars is no longer a question of “if,” but “when.”


Leave a Reply